胡壮麟《语言学教程》(修订版)
学习指导
第二部分 重点章节测试题
Test One: Invitations to Linguistics
I. Choose the best answer. (20%)
1. Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human __________.
A. contact B. communication C. relation D. community
2. Which of the following words is entirely arbitrary?
A. tree B. typewriter C. crash D. bang
3. The function of the sentence “Water boils at 100 degrees Centigrade.” is __________.
A. interrogative B. directive C. informative D. performative
4. In Chinese when someone breaks a bowl or a plate the host or the people present are likely to say“碎碎(岁岁)平安”as a means of controlling the forces which they believes feel might affect their lives. Which functions does it perform?
A. Interpersonal B. Emotive C. Performative D. Recreational
5. Which of the following property of language enables language users to overcome the barriers caused by time and place, due to this feature of language, speakers of a language are free to talk about anything in any situation?
A. Transferability B. Duality C. Displacement D. Arbitrariness
6. Study the following dialogue. What function does it play according to the functions of language?
— A nice day, isn’t it?
— Right! I really enjoy the sunlight.
A. Emotive B. Phatic C. Performative D. Interpersonal
7. __________ refers to the actual realization of the ideal language user’s knowledge of the rules of his language in utterances.
A. Performance B. Competence C. Langue D. Parole
8. When a dog is barking, you assume it is barking for something or at someone that exists hear and now. It couldn’t be sorrowful for some lost love or lost bone. This indicates the design feature of __________.
A. cultural transmission B. productivity C. displacement D. duality
9. __________ answers such questions as how we as infants acquire our first language.
A. Psycholinguistics B. Anthropological linguistics
C. Sociolinguistics D. Applied linguistics
10. __________ deals with language application to other fields, particularly education.
A. Linguistic theory B. Practical linguistics
C. Applied linguistics D. Comparative linguistics
II. Decide whether the following statements are true or false. (10%)
11. Language is a means of verbal communication. Therefore, the communication way used by the deaf-mute is not language.
12. Language change is universal, ongoing and arbitrary.
13. Speaking is the quickest and most efficient way of the human communication systems.
14. Language is written because writing is the primary medium for all languages.
15. We were all born with the ability to acquire language, which means the details of any language system can be genetically transmitted.
16. Only human beings are able to communicate.
17. F. de Saussure, who made the distinction between langue and parole in the early 20th century, was a French linguist.
18. A study of the features of the English used in Shakespeare’s time is an example of the diachronic study of language.
19. Speech and writing came into being at much the same time in human history.
20. All the languages in the world today have both spoken and written forms.
III. Fill in the blanks. (10%)
21. Language, broadly speaking, is a means of __________ communication.
22. In any language words can be used in new ways to mean new things and can be combined into innumerable sentences based on limited rules. This feature is usually termed __________.
23. Language has many functions. We can use language to talk about itself. This function is __________.
24. Theory that primitive man made involuntary vocal noises while performing heavy work has been called the __________ theory.
25. Linguistics is the __________ study of language.
26. Modern linguistics is __________ in the sense that the linguist tries to discover what language is rather than lay down some rules for people to observe.
27. One general principle of linguistic analysis is the primacy of __________ over writing.
28. The description of a language as it changes through time is a __________ study.
29. Saussure put forward two important concepts. __________ refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all members of a speech community.
30. Linguistic potential is similar to Saussure’s langue and Chomsky’s __________.
IV. Explain the following terms, using examples. (20%)
31. Design feature
32. Displacement
33. Competence
34. Synchronic linguistics
V. Answer the following questions. (20%)
35. Why do people take duality as one of the important design features of human language? Can you tell us what language will be if it has no such design feature? (南开大学,2004)
36. Why is it difficult to define language? (北京第二外国语大学,2004)
VI. Analyze the following situation. (20%)
37. How can a linguist make his analysis scientific? (青岛海洋大学,1999)
Test Two: Phonetics and Phonology
I. Choose the best answer. (20%)
1. Pitch variation is known as __________ when its patterns are imposed on sentences.
A. intonation B. tone C. pronunciation D. voice
2. Conventionally a __________ is put in slashes (/ /).
A. allophone B. phone C. phoneme D. morpheme
3. An aspirated p, an unaspirated p and an unreleased p are __________ of the p phoneme.
A. analogues B. tagmemes C. morphemes D. allophones
4. The opening between the vocal cords is sometimes referred to as __________.
A. glottis B. vocal cavity C. pharynx D. uvula
5. The diphthongs that are made with a movement of the tongue towards the center are known as __________ diphthongs.
A. wide B. closing C. narrow D. centering
6. A phoneme is a group of similar sounds called __________.
A. minimal pairs B. allomorphs C. phones D. allophones
7. Which branch of phonetics concerns the production of speech sounds?
A. Acoustic phonetics B. Articulatory phonetics
C. Auditory phonetics D. None of the above
8. Which one is different from the others according to places of articulation?
A. [n] B. [m] C. [b] D. [p]
9. Which vowel is different from the others according to the characteristics of vowels?
A. [i:] B. [u] C. [e] D. [i]
10. What kind of sounds can we make when the vocal cords are vibrating?
A. Voiceless B. Voiced C. Glottal stop D. Consonant
II. Decide whether the following statements are true or false. (10%)
11. Suprasegmental phonology refers to the study of phonological properties of units larger than the segment-phoneme, such as syllable, word and sentence.
12. The air stream provided by the lungs has to undergo a number of modification to acquire the quality of a speech sound.
13. Two sounds are in free variation when they occur in the same environment and do not contrast, namely, the substitution of one for the other does not produce a different word, but merely a different pronunciation.
14. [p] is a voiced bilabial stop.
15. Acoustic phonetics is concerned with the perception of speech sounds.
16. All syllables must have a nucleus but not all syllables contain an onset and a coda.
17. When pure vowels or monophthongs are pronounced, no vowel glides take place.
18. According to the length or tenseness of the pronunciation, vowels can be divided into tense vs. lax or long vs. short.
19. Received Pronunciation is the pronunciation accepted by most people.
20. The maximal onset principle states that when there is a choice as to where to place a consonant, it is put into the coda rather than the onset.
III. Fill in the blanks. (20%)
21. Consonant sounds can be either __________ or __________, while all vowel sounds are __________.
22. Consonant sounds can also be made when two organs of speech in the mouth are brought close together so that the air is pushed out between them, causing __________.
23. The qualities of vowels depend upon the position of the __________ and the lips.
24. One element in the description of vowels is the part of the tongue which is at the highest point in the mouth. A second element is the __________ to which that part of the tongue is raised.
25. Consonants differ from vowels in that the latter are produced without __________.
26. In phonological analysis the words fail / veil are distinguishable simply because of the two phonemes /f/ - /v/. This is an example for illustrating __________.
27. In English there are a number of __________, which are produced by moving from one vowel position to another through intervening positions.
28. __________ refers to the phenomenon of sounds continually show the influence of their neighbors.
29. __________ is the smallest linguistic unit.
30. Speech takes place when the organs of speech move to produce patterns of sound. These movements have an effect on the __________ coming from the lungs.
IV. Explain the following terms, using examples. (20%)
31. Sound assimilation
32. Suprasegmental feature
33. Complementary distribution
34. Distinctive features
V. Answer the following questions. (20%)
35. What is acoustic phonetics?(中国人民大学,2003)
36. What are the differences between voiced sounds and voiceless sounds in terms of articulation?(南开大学,2004)
VI. Analyze the following situation. (20%)
37. Write the symbol that corresponds to each of the following phonetic descriptions; then give an English word that contains this sound. Example: voiced alveolar stop [d] dog. (青岛海洋大学,1999)
(1) voiceless bilabial unaspirated stop
(2) low front vowel
(3) lateral liquid
(4) velar nasal
(5) voiced interdental fricative
Test Three: Morphology
I. Choose the best answer. (20%)
1. Nouns, verbs and adjectives can be classified as __________.
A. lexical words B. grammatical words C. function words D. form words
2. Morphemes that represent tense, number, gender and case are called __________ morpheme.
A. inflectional B. free C. bound D. derivational
3. There are __________ morphemes in the word denationalization.
A. three B. four C. five D. six
4. In English –ise and –tion are called __________.
A. prefixes B. suffixes C. infixes D. stems
5. The three subtypes of affixes are: prefix, suffix and __________.
A. derivational affix B. inflectional affix C. infix D. back-formation
6. __________ is a way in which new words may be formed from already existing words by subtracting an affix which is thought to be part of the old word.
A. affixation B. back-formation C. insertion D. addition
7. The word TB is formed in the way of __________.
A. acronymy B. clipping C. initialism D. blending
8. The words like comsat and sitcom are formed by __________.
A. blending B. clipping C. back-formation D. acronymy
9. The stem of disagreements is __________.
A. agreement B. agree C. disagree D. disagreement
10. All of them are meaningful except for __________.
A. lexeme B. phoneme C. morpheme D. allomorph
II. Decide whether the following statements are true or false. (10%)
11. Phonetically, the stress of a compound always falls on the first element, while the second element receives secondary stress.
胡壮麟语言学教程大纲分析及试题
本站小编 免费考研网/2019-03-17
相关话题/语言学
语言学纲要学习指导书练习答案(整理版)
《语言学概论》学习辅导书参考答案(导言) 一、名词解释(20分,每小题4分) 1.语言学:就是以语言为研究对象的科学,研究语言的本质、语言的结构和发展规律。 2.小学:指我国传统的语文学,包括文字学、音韵学、训诂学三方面的内容。 3.专语语言学:也叫具体语言学、个别语言学,以一种(或几种有联系的)语言 ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2019-02-13华师语言所学硕2019年语言学概论考研真题
一、填空题所谓递归性,是指相同的结构规则可以( ),可以由( )扩展成层层嵌套的( )。语言系统可以分为( )、( )、( )等子系统。黏着语又称( ),其特点是通过附加多种( )来表示各种( )。音质的不同取决于三方面的条件:一是( ),二是( ),三是( )的形状。根据义项之间不同的关 ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2019-01-03丁言仁《英语语言学纲要》笔记和课后习题详解
目录封面内容简介目录第1章 我们身边的语言 1.1 复习笔记 1.2 课后习题详解第2章 英语语法 2.1 复习笔记 2.2 课后习题详解第3章 英语语音系统和书写系统 3.1 复习笔记 3.2 课后习题详解第4章 英语语义和词汇 4.1 复习笔记 4.2 课后习题详解第5章 语言在语境中的应用 5 ...辅导考试考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-30扬州大学文学院816语言学理论历年考研真题汇编
目录封面内容简介目录2014年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题2015年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题2016年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题2017年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题2018年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题内容简介本书收录了扬州大学文学院&ldq ...辅导考试考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-30江西师范大学文学院语言学概论历年考研真题汇编
目录封面内容简介目录2012年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2013年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2014年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2015年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2016年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2017年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题内容 ...辅导考试考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-30日本语言学校介绍及之后的升学之路
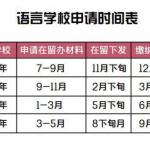 随着大量留学生涌入日本,日本的语言学校可以说是遍地开花。很多学生和家长对语言学校始终保持疑虑,担心在日本读语言学校对学生升学帮助不大还浪费时间,今天小编就系统的介绍一下日本的语言学校及语言学校毕业后如何申请修士。 语言学校的作用: 1. 学日语: 顾名思义,语言学校是学日语的地方,如果日语不 ...日本留学 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-18
随着大量留学生涌入日本,日本的语言学校可以说是遍地开花。很多学生和家长对语言学校始终保持疑虑,担心在日本读语言学校对学生升学帮助不大还浪费时间,今天小编就系统的介绍一下日本的语言学校及语言学校毕业后如何申请修士。 语言学校的作用: 1. 学日语: 顾名思义,语言学校是学日语的地方,如果日语不 ...日本留学 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-182019年北京邮电大学817英语语言学与文学基础考研大纲
817英语语言学与文学基础一、考试要求要求考生系统地掌握大学本科期间所学的语言学概论和英美文学的基本概念和知识,并且语言学方向考生能够运用语言学基本规则和理论分析一般的语言现象,文学方向考生能够运用所学知识对作家、作品和文学人物进行初步的分析、批判。二、考试内容语言的概念、特征以及各分支的概念、研究 ...专业课大纲 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年浙江财经大学语言学概论和现代汉语考研初试大纲
《语言学概论和现代汉语》考试大纲一、考试目的和要求本课程涵盖汉语言文学专业本科阶段现代汉语和语言学概论的主要内容,是汉语言文学专业的核心课程,也是汉语言文字学专业学生必须掌握的基础性课程。考试目的:测试学生运用语言理论分析和解决语言问题的基本能 ...专业课大纲 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年浙江财经大学语言学理论考研初试大纲
《语言学理论》考试大纲一、考试目的和要求本课程涵盖汉语言文学专业本科阶段语言学概论的主要内容,是汉语言文学专业的核心课程,也是汉语言文字学专业学生必须掌握的基础性课程。考试目的:测试学生运用语言理论分析和解决语言问题的基本能力,并由此判断学生是否具有进一步深造的基本素质和 ...专业课大纲 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年华侨大学810语言学概论考研初试大纲
2019年华侨大学硕士研究生招生考试初试自命题科目考试大纲招生学院: 华文学院 招生专业: 华语与华文教育科目名称: 语言学概论一、考试形式与试卷结构(一)试卷满分值及考试时间本试卷满分为150分,考试时间为180分钟。(二)答题方式答题方式为闭卷、笔试。试卷由试题和答题纸组成;答案必须写在答题纸( ...专业课大纲 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年广东外语外贸大学050102语言学及应用语言学考研专业目录
据广东外语外贸大学研究生院消息,2019年广东外语外贸大学050102语言学及应用语言学考研专业目录已经公布,详情如下: ...专业目录 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年广东外语外贸大学050211外国语言学及应用语言学考研专业目录
据广东外语外贸大学研究生院消息,2019年广东外语外贸大学050211外国语言学及应用语言学考研专业目录已经公布,详情如下: ...专业目录 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-04山东师范大学外国语学院818英语语言学及应用语言学基础(含英语语言学、应用语言学与英语教学基础知识)历年考研真题及详解
目录封面内容简介目录2017年山东师范大学818英语语言学及应用语言学基础考研真题及详解2018年山东师范大学818英语语言学及应用语言学基础考研真题及详解内容简介本书收集了山东师范大学外国语学院英语语言学及应用语言学基础(含英语语言学、应用语言学与英语教学基础知识)20 ...辅导考试考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-02南开大学2010年语言学概论考研真题
 2010年语言学概论真题答案 一.举例并解释 1.孤立语(知识点:书P112) 根据词的结构划分出来的一种语言类型,也叫词根语,指没有构形语素或基本无构形语素的语言。词不发生语法形式变化,语序和虚词成为基本的语法形式。如:汉语、越南语。 2.音位变体(知识点:书P71) 音位变体是属于一个音位的各 ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-08-26
2010年语言学概论真题答案 一.举例并解释 1.孤立语(知识点:书P112) 根据词的结构划分出来的一种语言类型,也叫词根语,指没有构形语素或基本无构形语素的语言。词不发生语法形式变化,语序和虚词成为基本的语法形式。如:汉语、越南语。 2.音位变体(知识点:书P71) 音位变体是属于一个音位的各 ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-08-26日本语言学校怎么样?日本语言学校考察实录
 启程 2017年5月9日,在北京首都国际机场跟男神博士见面,马上就要启程,真是心潮澎湃,愉悦的因子在身边跳跃。同博士在机场换了部分日币,就匆匆赶往登机处,开启了日本学校探访之行 抵达 下午2点到达日本成田国际机场,刚下飞机,就收到热心的双叶外国语老师的信息,已然在出口等待我们,当然同行的还有其他的老师。 ...日本留学 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-08-24
启程 2017年5月9日,在北京首都国际机场跟男神博士见面,马上就要启程,真是心潮澎湃,愉悦的因子在身边跳跃。同博士在机场换了部分日币,就匆匆赶往登机处,开启了日本学校探访之行 抵达 下午2点到达日本成田国际机场,刚下飞机,就收到热心的双叶外国语老师的信息,已然在出口等待我们,当然同行的还有其他的老师。 ...日本留学 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-08-24


