胡壮麟语言学教程大纲分析及试题(5)
本站小编 免费考研网/2019-03-17
In terms of truth value, the following relationships exist between these two sentences: when A is true, B must be also true; when B is false, A must also be false. When B is true, A may be true or false. Therefore we can say A entails B.
32. Proposition: It is the result of the abstraction of sentences, which are descriptions of states of affairs and which some writers see as a basic element of sentence meaning. For example, the two sentences “Caesar invaded Gaul” and “Gaul was invaded by Caesar” hold the same proposition.
33. Compositional analysis: It defines the meaning of a lexical element in terms of semantic components, or semantic features. For example, the meaning of the word boy may be analyzed into three components: HUMAN, YOUNG and MALE. Similarly girl may be analyzed into HUMAN, YOUNG and FEMALE.
34. Reference: It is what a linguistic form refers to in the real world; it is a matter of the relationship between the form and the reality.
V.
35.
Hyponymy, metonymy or part-whole relationship
36.
(Omit.)
VI.
37.
(1) The (a) words and (b) words are male.
The (a) words are human, while the (b) words are non-human.
(2) The (a) words and (b) words are inanimate.
The (a) words are instrumental, while the (b) words are edible.
(3) The (a) words and (b) words are worldly or conceptual.
The (a) words are material, while the (b) words are spiritual.
Test Six
I.
1~5 DBCBA 6~10 CBCAD
II.
11~15 FTTFF 16~20 FFFTT
III.
21. context 22. utterance
23. abstract 24. Constatives
25. Performatives 26. locutionary
27. illocutionary 28. commissive
29. expressive 30. quantity
IV.
31. Conversational implicature: In our daily life, speakers and listeners involved in conversation are generally cooperating with each other. In other words, when people are talking with each other, they must try to converse smoothly and successfully. In accepting speakers’ presuppositions, listeners have to assume that a speaker is not trying to mislead them. This sense of cooperation is simply one in which people having a conversation are not normally assumed to be trying to confuse, trick, or withhold relevant information from one another. However, in real communication, the intention of the speaker is often not the literal meaning of what he or she says. The real intention implied in the words is called conversational implicature.
32. Performative: In speech act theory an utterance which performs an act, such as Watch out (= a warning).
33. Locutionary act: A locutionary act is the saying of something which is meaningful and can be understood.
34. Horn’s Q-principle: (1) Make your contribution sufficient (cf. quantity); (2) Say as much as you can (given R).
V.
35.
Pragmatics is the study of the use of language in communication, particularly the relationships between sentences and the contexts and situations in which they are used. Pragmatics includes the study of
(1) How the interpretation and use of utterances depends on knowledge of the real world;
(2) How speakers use and understand speech acts;
(3) How the structure of sentences is influenced by the relationship between the speaker and the hearer.
Pragmatics is sometimes contrasted with semantics, which deals with meaning without reference to the users and communicative functions of sentences.
36.
Yes, B is cooperative. On the face of it, B’s statement is not an answer to A’s question. B doesn’t say “when.” However, A will immediately interpret the statement as meaning “I don’t know” or “I am not sure.” Just assume that B is being “relevant” and “informative.” Given that B’s answer contains relevant information, A can work out that “an accident further up the road” conventionally involves “traffic jam,” and “traffic jam” preludes “bus coming.” Thus, B’s answer is not simply a statement of “when the bus comes”; it contains an implicature concerning “when the bus comes.”
VI.
37.
It occurs before and / or after a word, a phrase or even a longer utterance or a text. The context often helps in understanding the particular meaning of the word, phrase, etc.
The context may also be the broader social situation in which a linguistic item is used.
(1)
a. A mild criticism of someone who should have cleaned the room.
b. In a language class where a student made a mistake, for he intended to say “tidy.”
c. The room was wanted for a meeting.
(2)
a. A mild way to express disagreement with someone who has complimented on a lady’s appearance.
b. A regret that the customer had not taken the dress.
c. That she wore a red shirt was not in agreement with the custom on the occasion.
Test Seven
I.
1~5 BCAAC 6~10 DACAD
II.
11~15 FTFFF 16~20 TFTFF
III.
21. community 22. variety
23. dialectal 24. planning
25. sociolects 26. Stylistic
27. official 28. superposed
29. vernacular 30. inflectional
IV.
31. Lingua franca: A lingua franca is a variety of language that serves as a common speech for social contact among groups of people who speaks different native languages or dialects.
32. Regional dialect: Regional dialect, also social or class dialect, is a speech variety spoken by the members of a particular group or stratum of a speech community.
33. Register: Register, also situational dialect, refers to the language variety appropriate for use in particular speech situations on which degrees of formality depends.
34. Sociolinguistics: Defined in its broadest way, sociolinguistics, a subdiscipline of linguistics, is the study of language in relation to society. It is concerned with language variation, language use, the impact of extra-linguistic factors on language use, etc.
V.
35.
American English is not superior to African English. As different branches of English, African English and American English are equal. Similar as they are, they are influenced by their respective cultural context and thus form respective systems of pronunciation, words and even grammar.
36.
In China, Chinese has a more strict and complex relationship system. So in Chinese there are a lot more kinship words than in English.
VI.
37.
(Omit.)
Test Eight
I.
1~5 BACAA 6~10 ABDCC
II.
11~15 FFTTF 16~20 FTTTF
III.
21. synchronic 22. phonetics
23. J. R. Firth 24. systemic
25. sociologically 26. distribution
27. Bloomfieldian 28. Descriptivism
29. innateness 30. hypothesis-maker
IV.
31. FSP: It stands for Functional Sentence Perspective. It is a theory of linguistic analysis which refers to an analysis of utterances (or texts) in terms of the information they contain.
32. Cohesion: The Cohesion shows whether a certain tagmeme is dominating other tagmemes or is dominated by others.
33. LAD: LAD, that is Language Acquisition Device, is posited by Chomsky in the 1960s as a device effectively present in the minds of children by which a grammar of their native language is constructed.
34. Case Grammar: It is an approach that stresses the relationship of elements in a sentence. It is a type of generative grammar developed by C. J. Fillmore in the late 1960s.
V. VI. Omit.
相关话题/语言学
语言学纲要学习指导书练习答案(整理版)
《语言学概论》学习辅导书参考答案(导言) 一、名词解释(20分,每小题4分) 1.语言学:就是以语言为研究对象的科学,研究语言的本质、语言的结构和发展规律。 2.小学:指我国传统的语文学,包括文字学、音韵学、训诂学三方面的内容。 3.专语语言学:也叫具体语言学、个别语言学,以一种(或几种有联系的)语言 ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2019-02-13华师语言所学硕2019年语言学概论考研真题
一、填空题所谓递归性,是指相同的结构规则可以( ),可以由( )扩展成层层嵌套的( )。语言系统可以分为( )、( )、( )等子系统。黏着语又称( ),其特点是通过附加多种( )来表示各种( )。音质的不同取决于三方面的条件:一是( ),二是( ),三是( )的形状。根据义项之间不同的关 ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2019-01-03丁言仁《英语语言学纲要》笔记和课后习题详解
目录封面内容简介目录第1章 我们身边的语言 1.1 复习笔记 1.2 课后习题详解第2章 英语语法 2.1 复习笔记 2.2 课后习题详解第3章 英语语音系统和书写系统 3.1 复习笔记 3.2 课后习题详解第4章 英语语义和词汇 4.1 复习笔记 4.2 课后习题详解第5章 语言在语境中的应用 5 ...辅导考试考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-30扬州大学文学院816语言学理论历年考研真题汇编
目录封面内容简介目录2014年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题2015年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题2016年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题2017年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题2018年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题内容简介本书收录了扬州大学文学院&ldq ...辅导考试考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-30江西师范大学文学院语言学概论历年考研真题汇编
目录封面内容简介目录2012年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2013年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2014年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2015年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2016年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2017年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题内容 ...辅导考试考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-30日本语言学校介绍及之后的升学之路
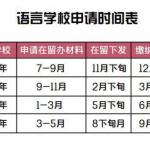 随着大量留学生涌入日本,日本的语言学校可以说是遍地开花。很多学生和家长对语言学校始终保持疑虑,担心在日本读语言学校对学生升学帮助不大还浪费时间,今天小编就系统的介绍一下日本的语言学校及语言学校毕业后如何申请修士。 语言学校的作用: 1. 学日语: 顾名思义,语言学校是学日语的地方,如果日语不 ...日本留学 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-18
随着大量留学生涌入日本,日本的语言学校可以说是遍地开花。很多学生和家长对语言学校始终保持疑虑,担心在日本读语言学校对学生升学帮助不大还浪费时间,今天小编就系统的介绍一下日本的语言学校及语言学校毕业后如何申请修士。 语言学校的作用: 1. 学日语: 顾名思义,语言学校是学日语的地方,如果日语不 ...日本留学 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-182019年北京邮电大学817英语语言学与文学基础考研大纲
817英语语言学与文学基础一、考试要求要求考生系统地掌握大学本科期间所学的语言学概论和英美文学的基本概念和知识,并且语言学方向考生能够运用语言学基本规则和理论分析一般的语言现象,文学方向考生能够运用所学知识对作家、作品和文学人物进行初步的分析、批判。二、考试内容语言的概念、特征以及各分支的概念、研究 ...专业课大纲 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年浙江财经大学语言学概论和现代汉语考研初试大纲
《语言学概论和现代汉语》考试大纲一、考试目的和要求本课程涵盖汉语言文学专业本科阶段现代汉语和语言学概论的主要内容,是汉语言文学专业的核心课程,也是汉语言文字学专业学生必须掌握的基础性课程。考试目的:测试学生运用语言理论分析和解决语言问题的基本能 ...专业课大纲 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年浙江财经大学语言学理论考研初试大纲
《语言学理论》考试大纲一、考试目的和要求本课程涵盖汉语言文学专业本科阶段语言学概论的主要内容,是汉语言文学专业的核心课程,也是汉语言文字学专业学生必须掌握的基础性课程。考试目的:测试学生运用语言理论分析和解决语言问题的基本能力,并由此判断学生是否具有进一步深造的基本素质和 ...专业课大纲 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年华侨大学810语言学概论考研初试大纲
2019年华侨大学硕士研究生招生考试初试自命题科目考试大纲招生学院: 华文学院 招生专业: 华语与华文教育科目名称: 语言学概论一、考试形式与试卷结构(一)试卷满分值及考试时间本试卷满分为150分,考试时间为180分钟。(二)答题方式答题方式为闭卷、笔试。试卷由试题和答题纸组成;答案必须写在答题纸( ...专业课大纲 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年广东外语外贸大学050102语言学及应用语言学考研专业目录
据广东外语外贸大学研究生院消息,2019年广东外语外贸大学050102语言学及应用语言学考研专业目录已经公布,详情如下: ...专业目录 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年广东外语外贸大学050211外国语言学及应用语言学考研专业目录
据广东外语外贸大学研究生院消息,2019年广东外语外贸大学050211外国语言学及应用语言学考研专业目录已经公布,详情如下: ...专业目录 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-04山东师范大学外国语学院818英语语言学及应用语言学基础(含英语语言学、应用语言学与英语教学基础知识)历年考研真题及详解
目录封面内容简介目录2017年山东师范大学818英语语言学及应用语言学基础考研真题及详解2018年山东师范大学818英语语言学及应用语言学基础考研真题及详解内容简介本书收集了山东师范大学外国语学院英语语言学及应用语言学基础(含英语语言学、应用语言学与英语教学基础知识)20 ...辅导考试考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-02南开大学2010年语言学概论考研真题
 2010年语言学概论真题答案 一.举例并解释 1.孤立语(知识点:书P112) 根据词的结构划分出来的一种语言类型,也叫词根语,指没有构形语素或基本无构形语素的语言。词不发生语法形式变化,语序和虚词成为基本的语法形式。如:汉语、越南语。 2.音位变体(知识点:书P71) 音位变体是属于一个音位的各 ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-08-26
2010年语言学概论真题答案 一.举例并解释 1.孤立语(知识点:书P112) 根据词的结构划分出来的一种语言类型,也叫词根语,指没有构形语素或基本无构形语素的语言。词不发生语法形式变化,语序和虚词成为基本的语法形式。如:汉语、越南语。 2.音位变体(知识点:书P71) 音位变体是属于一个音位的各 ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-08-26日本语言学校怎么样?日本语言学校考察实录
 启程 2017年5月9日,在北京首都国际机场跟男神博士见面,马上就要启程,真是心潮澎湃,愉悦的因子在身边跳跃。同博士在机场换了部分日币,就匆匆赶往登机处,开启了日本学校探访之行 抵达 下午2点到达日本成田国际机场,刚下飞机,就收到热心的双叶外国语老师的信息,已然在出口等待我们,当然同行的还有其他的老师。 ...日本留学 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-08-24
启程 2017年5月9日,在北京首都国际机场跟男神博士见面,马上就要启程,真是心潮澎湃,愉悦的因子在身边跳跃。同博士在机场换了部分日币,就匆匆赶往登机处,开启了日本学校探访之行 抵达 下午2点到达日本成田国际机场,刚下飞机,就收到热心的双叶外国语老师的信息,已然在出口等待我们,当然同行的还有其他的老师。 ...日本留学 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-08-24


