胡壮麟语言学教程大纲分析及试题(4)
本站小编 免费考研网/2019-03-17
A. Stratificational B. Case C. Relational D. Montague
7. In Halliday’s view, the __________ function is the function that the child uses to know about his surroundings.
A. personal B. heuristic C. imaginative D. informative
8. The rheme in the sentence “On it stood Jane” is __________.
A. On it B. stood C. On it stood D. Jane
9. Chomsky follows __________ in philosophy and mentalism in psychology.
A. empiricism B. behaviorism C. relationalism D. mentalism
10. TG grammar has seen __________ stages of development.
A. three B. four C. five D. six
II. Decide whether the following statements are true or false. (10%)
11. Following Saussure’s distinction between langue and parole, Trubetzkoy argued that phonetics belonged to langue whereas phonology belonged to parole.
12. The subject-predicate distinction is the same as the theme and rheme contrast.
13. London School is also known as systemic linguistics and functional linguistics.
14. According to Firth, a system is a set of mutually exclusive options that come into play at some point in a linguistic structure.
15. American Structuralism is a branch of diachronic linguistics that emerged independently in the United States at the beginning of the twentieth century.
16. The Standard Theory focuses discussion on language universals and universal grammar.
17. American descriptive linguistics is empiricist and focuses on diversities of languages.
18. Chomsky’s concept of linguistic performance is similar to Saussure’s concept of parole, while his use of linguistic competence is somewhat different from Saussure’s langue.
19. Glossematics emphasizes the nature and status of linguistic theory and its relation to description.
20. If two sentences have exactly the same ideational and interpersonal functions, they would be the same in terms of textual coherence.
III. Fill in the blanks. (20%)
21. The Prague School practiced a special style of __________ Linguistics.
22. The Prague School is best known and remembered for its contribution to phonology and the distinction between __________ and phonology.
23. The man who turned linguistics proper into a recognized distinct academic subject in Britain was __________.
24. Halliday’s Systemic Grammar contains a functional component, and the theory behind his Functional Grammar is __________.
25. Systemic-Functional Grammar is a(n) __________ oriented functional linguistic approach.
26. Structuralism is based on the assumption that grammatical categories should be defined not in terms of meaning but in terms of __________.
27. In the history of American linguistics, the period between 1933 and 1950 is also known as __________ Age.
28. __________ in language theories is characteristic of America.
29. The starting point of Chomsky’s TG grammar is his __________ hypothesis.
30. Chomsky argues that LAD probably consists of three elements, that is a __________, linguistic universal, and an evaluation procedure.
IV. Explain the following terms, using examples. (20%)
31. FSP
32. Cohesion
33. LAD
34. Case Grammar
V. Answer the following questions. (20%)
35. Why is Saussure hailed as the father of modern linguistics?
36. What is behaviorism? What is behaviorism in linguistics? What is the relationship between linguistics and behaviorism according to Bloomfield? Does behaviorism have any limitations? If yes, what are they?
VI. Analyze the following situation. (20%)
37. Can you make a brief introduction to some important schools and their influential representatives in modern linguistics?
第二部分结束
第三部分 测试题参考答案
[In the reference keys, I won’t give examples or further analysis. That seems too much work for me. Therefore, this key is only for reference. In order to answer this kind of question, you need more examples. So you should read the textbook carefully. – icywarmtea]
Test One
I.
1~5 BACCC 6~10 BACAC
II.
11~15 FFTFF 16~20 FFFFF
III.
21. verbal 22. productivity / creativity
23. metalingual function 24. yo-he-ho
25. scientific 26. descriptive
27. speech 28. diachronic linguistic
29. langue 30. competence
IV.
31. Design feature: It refers to the defining properties of human language that tell the difference between human language and any system of animal communication.
32. Displacement: It means that human languages enable their users to symbolize objects, events and concepts, which are not present (in time and space) at the moment of communication.
33. Competence: It is an essential part of performance. It is the speaker’s knowledge of his or her language; that is, of its sound structure, its words, and its grammatical rules. Competence is, in a way, an encyclopedia of language. Moreover, the knowledge involved in competence is generally unconscious. A transformational-generative grammar is a model of competence.
34. Synchronic linguistics: It refers to the study of a language at a given point in time. The time studied may be either the present or a particular point in the past; synchronic analyses can also be made of dead languages, such as Latin. Synchronic linguistics is contrasted with diachronic linguistics, the study of a language over a period of time.
V.
35.
Duality makes our language productive. A large number of different units can be formed out of a small number of elements – for instance, tens of thousands of words out of a small set of sounds, around 48 in the case of the English language. And out of the huge number of words, there can be astronomical number of possible sentences and phrases, which in turn can combine to form unlimited number of texts. Most animal communication systems do not have this design feature of human language.
If language has no such design feature, then it will be like animal communicational system which will be highly limited. It cannot produce a very large number of sound combinations, e.g. words, which are distinct in meaning.
36.
It is difficult to define language, as it is such a general term that covers too many things. Thus, definitions for it all have their own special emphasis, and are not totally free from limitations.
VI.
37.
It should be guided by the four principles of science: exhaustiveness, consistency, economy and objectivity and follow the scientific procedure: form hypothesis – collect data – check against the observable facts – come to a conclusion.
Test Two
I.
1~5 ACDAA 6~10 DBABB
II.
11~15 TTTFF 16~20 TTTFF
III.
21. voiced, voiceless, voiced 22. friction
23. tongue 24. height
25. obstruction 26. minimal pairs
27. diphthongs 28. Co-articulation
29. Phonemes 30. air stream
IV.
31. Sound assimilation: Speech sounds seldom occur in isolation. In connected speech, under the influence of their neighbors, are replaced by other sounds. Sometimes two neighboring sounds influence each other and are replaced by a third sound which is different from both original sounds. This process is called sound assimilation.
32. Suprasegmental feature: The phonetic features that occur above the level of the segments are called suprasegmental features; these are the phonological properties of such units as the syllable, the word, and the sentence. The main suprasegmental ones includes stress, intonation, and tone.
33. Complementary distribution: The different allophones of the same phoneme never occur in the same phonetic context. When two or more allophones of one phoneme never occur in the same linguistic environment they are said to be in complementary distribution.
34. Distinctive features: It refers to the features that can distinguish one phoneme from another. If we can group the phonemes into two categories: one with this feature and the other without, this feature is called a distinctive feature.
V.
35.
Acoustic phonetics deals with the transmission of speech sounds through the air. When a speech sound is produced it causes minor air disturbances (sound waves). Various instruments are used to measure the characteristics of these sound waves.
36.
When the vocal cords are spread apart, the air from the lungs passes between them unimpeded. Sounds produced in this way are described as voiceless; consonants [p, s, t] are produced in this way. But when the vocal cords are drawn together, the air from the lungs repeatedly pushes them apart as it passes through, creating a vibration effect. Sounds produced in this way are described as voiced. [b, z, d] are voiced consonants.
VI.
37.
Omit.
Test Three
I.
1~5 AACBB 6~10 BCADB
II.
11~15 TTFTT 16~20 FTFFF
III.
21. initialism, acronym 22. vocabulary
23. solid, hyphenated, open 24. morpheme
25. close, open 26. back-formation
27. conversion 28. morpheme
29. derivative, compound 30. affix, bound root
IV.
31. Blending: It is a process of word-formation in which a new word is formed by combining the meanings and sounds of two words, one of which is not in its full form or both of which are not in their full forms, like newscast (news + broadcast), brunch (breakfast + lunch)
32. Allomorph: It is any of the variant forms of a morpheme as conditioned by position or adjoining sounds.
33. Close-class word: It is a word whose membership is fixed or limited. Pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles, etc. are all closed-class words.
34. Morphological rule: It is the rule that governs which affix can be added to what type of base to form a new word, e.g. –ly can be added to a noun to form an adjective.
V.
Omit.
VI.
37.
(1) c (2) a (3) e (4) d (5) b
Test Four
I.
1~5 DCDDD 6~10 ADDBA
II.
11~15 TTTTF 16~20 FTFTT
III.
21. simple 22. sentence
23. subject 24. predicate
25. complex 26. embedded
27. open 28. Adjacency
29. Parameters 30. Case
IV.
31. Syntax: Syntax refers to the rules governing the way words are combined to form sentences in a language, or simply, the study of the formation of sentences.
32. IC analysis: Immediate constituent analysis, IC analysis for short, refers to the analysis of a sentence in terms of its immediate constituents – word groups (phrases), which are in turn analyzed into the immediate constituents of their own, and the process goes on until the ultimate sake of convenience.
33. Hierarchical structure: It is the sentence structure that groups words into structural constituents and shows the syntactic category of each structural constituent, such as NP, VP and PP.
34. Trace theory: After the movement of an element in a sentence there will be a trace left in the original position. This is the notion trace in T-G grammar. It’s suggested that if we have the notion trace, all the necessary information for semantic interpretation may come from the surface structure. E.g. The passive Dams are built by beavers. differs from the active Beavers built dams. in implying that all dams are built by beavers. If we add a trace element represented by the letter t after built in the passive as Dams are built t by beavers, then the deep structure information that the word dams was originally the object of built is also captured by the surface structure. Trace theory proves to be not only theoretically significant but also empirically valid.
V.
35.
An endocentric construction is one whose distribution is functionally equivalent, or approaching equivalence, to one of its constituents, which serves as the center, or head, of the whole. A typical example is the three small children with children as its head. The exocentric construction, opposite to the first type, is defined negatively as a construction whose distribution is not functionally equivalent to any of its constituents. Prepositional phrasal like on the shelf are typical examples of this type.
36.
(1) more | beautiful flowers
(2) more beautiful | flowers
VI.
S
NP VP
Det. NP V NP Adv.
Det. N.
The student wrote a letter yesterday.
Test Five
I.
1~5 ABDDB 6~10 CACDA
II.
11~15 FFTFT 16~20 TFTTT
III.
21. Semantics 22. direct
23. Reference 24. synonyms
25. homophones 26. Relational
27. Componential 28. selectional
29. argument 30. naming
IV.
31. Entailment: It is basically a semantic relation (or logical implication), and it can be clarified with the following sentences:
a. Tom divorced Jane.
b. Jane was Tom’s wife.
相关话题/语言学
语言学纲要学习指导书练习答案(整理版)
《语言学概论》学习辅导书参考答案(导言) 一、名词解释(20分,每小题4分) 1.语言学:就是以语言为研究对象的科学,研究语言的本质、语言的结构和发展规律。 2.小学:指我国传统的语文学,包括文字学、音韵学、训诂学三方面的内容。 3.专语语言学:也叫具体语言学、个别语言学,以一种(或几种有联系的)语言 ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2019-02-13华师语言所学硕2019年语言学概论考研真题
一、填空题所谓递归性,是指相同的结构规则可以( ),可以由( )扩展成层层嵌套的( )。语言系统可以分为( )、( )、( )等子系统。黏着语又称( ),其特点是通过附加多种( )来表示各种( )。音质的不同取决于三方面的条件:一是( ),二是( ),三是( )的形状。根据义项之间不同的关 ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2019-01-03丁言仁《英语语言学纲要》笔记和课后习题详解
目录封面内容简介目录第1章 我们身边的语言 1.1 复习笔记 1.2 课后习题详解第2章 英语语法 2.1 复习笔记 2.2 课后习题详解第3章 英语语音系统和书写系统 3.1 复习笔记 3.2 课后习题详解第4章 英语语义和词汇 4.1 复习笔记 4.2 课后习题详解第5章 语言在语境中的应用 5 ...辅导考试考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-30扬州大学文学院816语言学理论历年考研真题汇编
目录封面内容简介目录2014年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题2015年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题2016年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题2017年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题2018年扬州大学文学院816语言学理论考研真题内容简介本书收录了扬州大学文学院&ldq ...辅导考试考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-30江西师范大学文学院语言学概论历年考研真题汇编
目录封面内容简介目录2012年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2013年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2014年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2015年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2016年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题2017年江西师范大学文学院语言学概论考研真题内容 ...辅导考试考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-30日本语言学校介绍及之后的升学之路
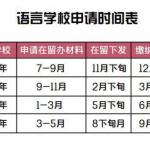 随着大量留学生涌入日本,日本的语言学校可以说是遍地开花。很多学生和家长对语言学校始终保持疑虑,担心在日本读语言学校对学生升学帮助不大还浪费时间,今天小编就系统的介绍一下日本的语言学校及语言学校毕业后如何申请修士。 语言学校的作用: 1. 学日语: 顾名思义,语言学校是学日语的地方,如果日语不 ...日本留学 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-18
随着大量留学生涌入日本,日本的语言学校可以说是遍地开花。很多学生和家长对语言学校始终保持疑虑,担心在日本读语言学校对学生升学帮助不大还浪费时间,今天小编就系统的介绍一下日本的语言学校及语言学校毕业后如何申请修士。 语言学校的作用: 1. 学日语: 顾名思义,语言学校是学日语的地方,如果日语不 ...日本留学 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-182019年北京邮电大学817英语语言学与文学基础考研大纲
817英语语言学与文学基础一、考试要求要求考生系统地掌握大学本科期间所学的语言学概论和英美文学的基本概念和知识,并且语言学方向考生能够运用语言学基本规则和理论分析一般的语言现象,文学方向考生能够运用所学知识对作家、作品和文学人物进行初步的分析、批判。二、考试内容语言的概念、特征以及各分支的概念、研究 ...专业课大纲 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年浙江财经大学语言学概论和现代汉语考研初试大纲
《语言学概论和现代汉语》考试大纲一、考试目的和要求本课程涵盖汉语言文学专业本科阶段现代汉语和语言学概论的主要内容,是汉语言文学专业的核心课程,也是汉语言文字学专业学生必须掌握的基础性课程。考试目的:测试学生运用语言理论分析和解决语言问题的基本能 ...专业课大纲 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年浙江财经大学语言学理论考研初试大纲
《语言学理论》考试大纲一、考试目的和要求本课程涵盖汉语言文学专业本科阶段语言学概论的主要内容,是汉语言文学专业的核心课程,也是汉语言文字学专业学生必须掌握的基础性课程。考试目的:测试学生运用语言理论分析和解决语言问题的基本能力,并由此判断学生是否具有进一步深造的基本素质和 ...专业课大纲 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年华侨大学810语言学概论考研初试大纲
2019年华侨大学硕士研究生招生考试初试自命题科目考试大纲招生学院: 华文学院 招生专业: 华语与华文教育科目名称: 语言学概论一、考试形式与试卷结构(一)试卷满分值及考试时间本试卷满分为150分,考试时间为180分钟。(二)答题方式答题方式为闭卷、笔试。试卷由试题和答题纸组成;答案必须写在答题纸( ...专业课大纲 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年广东外语外贸大学050102语言学及应用语言学考研专业目录
据广东外语外贸大学研究生院消息,2019年广东外语外贸大学050102语言学及应用语言学考研专业目录已经公布,详情如下: ...专业目录 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-042019年广东外语外贸大学050211外国语言学及应用语言学考研专业目录
据广东外语外贸大学研究生院消息,2019年广东外语外贸大学050211外国语言学及应用语言学考研专业目录已经公布,详情如下: ...专业目录 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-04山东师范大学外国语学院818英语语言学及应用语言学基础(含英语语言学、应用语言学与英语教学基础知识)历年考研真题及详解
目录封面内容简介目录2017年山东师范大学818英语语言学及应用语言学基础考研真题及详解2018年山东师范大学818英语语言学及应用语言学基础考研真题及详解内容简介本书收集了山东师范大学外国语学院英语语言学及应用语言学基础(含英语语言学、应用语言学与英语教学基础知识)20 ...辅导考试考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-11-02南开大学2010年语言学概论考研真题
 2010年语言学概论真题答案 一.举例并解释 1.孤立语(知识点:书P112) 根据词的结构划分出来的一种语言类型,也叫词根语,指没有构形语素或基本无构形语素的语言。词不发生语法形式变化,语序和虚词成为基本的语法形式。如:汉语、越南语。 2.音位变体(知识点:书P71) 音位变体是属于一个音位的各 ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-08-26
2010年语言学概论真题答案 一.举例并解释 1.孤立语(知识点:书P112) 根据词的结构划分出来的一种语言类型,也叫词根语,指没有构形语素或基本无构形语素的语言。词不发生语法形式变化,语序和虚词成为基本的语法形式。如:汉语、越南语。 2.音位变体(知识点:书P71) 音位变体是属于一个音位的各 ...专业课考研资料 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-08-26日本语言学校怎么样?日本语言学校考察实录
 启程 2017年5月9日,在北京首都国际机场跟男神博士见面,马上就要启程,真是心潮澎湃,愉悦的因子在身边跳跃。同博士在机场换了部分日币,就匆匆赶往登机处,开启了日本学校探访之行 抵达 下午2点到达日本成田国际机场,刚下飞机,就收到热心的双叶外国语老师的信息,已然在出口等待我们,当然同行的还有其他的老师。 ...日本留学 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-08-24
启程 2017年5月9日,在北京首都国际机场跟男神博士见面,马上就要启程,真是心潮澎湃,愉悦的因子在身边跳跃。同博士在机场换了部分日币,就匆匆赶往登机处,开启了日本学校探访之行 抵达 下午2点到达日本成田国际机场,刚下飞机,就收到热心的双叶外国语老师的信息,已然在出口等待我们,当然同行的还有其他的老师。 ...日本留学 本站小编 免费考研网 2018-08-24


